How hybrid cars work? Explanation
Introduction:
Hybrid cars have gained popularity in recent years as environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. But how do these innovative vehicles work, and what sets them apart from conventional cars? In this article, we'll delve into the inner workings of hybrid cars, exploring their unique technology, fuel-saving features, and environmental benefits.
1. Dual Power Sources:
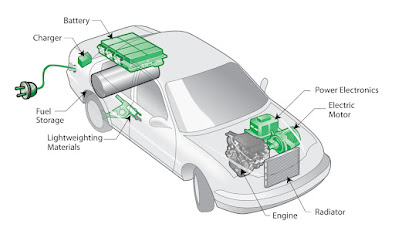
At the heart of a hybrid car is its dual powertrain system, which combines two distinct sources of propulsion: an internal combustion engine (usually gasoline-powered) and an electric motor. This combination allows hybrid cars to harness the strengths of both power sources while minimizing their weaknesses, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
2. Regenerative Braking:
One of the key features of hybrid cars is regenerative braking, which allows them to capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost during braking. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy and storing it in the car's battery pack. This stored energy can then be used to power the electric motor during acceleration, reducing the need for gasoline and improving overall fuel efficiency.
3. Seamless Transition:
Hybrid cars are designed to seamlessly transition between gasoline power and electric power, depending on driving conditions and power demands. At low speeds or during idling, the electric motor may take over propulsion duties, drawing power from the battery pack. As the vehicle's speed increases or when additional power is needed (such as during acceleration or climbing hills), the gasoline engine kicks in to provide additional power, either supplementing or replacing the electric motor's output.
4. Types of Hybrid Systems:
There are several types of hybrid systems used in hybrid cars, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits:
Series Hybrid: In a series hybrid, the gasoline engine acts solely as a generator, charging the battery pack and providing electricity to power the electric motor. The wheels are driven exclusively by the electric motor, resulting in zero-emission driving at low speeds.
Parallel Hybrid: In a parallel hybrid, both the gasoline engine and the electric motor are connected directly to the transmission, allowing them to work together to drive the wheels. This configuration offers greater flexibility and efficiency, as both power sources can contribute to propulsion simultaneously.
Plug-in Hybrid: Plug-in hybrids are equipped with larger battery packs that can be charged from an external power source, such as a wall outlet or charging station. This allows plug-in hybrids to travel longer distances on electric power alone, reducing reliance on gasoline and further improving fuel efficiency.
5. Environmental Benefits:
Hybrid cars offer numerous environmental benefits compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. By reducing fuel consumption and emissions, hybrid cars help mitigate air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, advances in hybrid technology have led to the development of plug-in hybrids and fully electric vehicles, further reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
Conclusion:
Hybrid cars represent a significant step forward in the quest for cleaner, more sustainable transportation solutions. By combining the efficiency of gasoline engines with the environmental benefits of electric propulsion, hybrid cars offer a compelling alternative to traditional vehicles. With their innovative technology, fuel-saving features, and environmental benefits, hybrid cars are paving the way for a greener, more sustainable future on the road.
How do hybrid cars work?
Hybrid cars work by combining two different power sources to propel the vehicle: an internal combustion engine (usually gasoline-powered) and an electric motor. These two power sources work together in various configurations to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and provide better overall performance. Here's a detailed explanation of how hybrid cars work:
1. Dual Powertrain System:
At the core of a hybrid car is its dual powertrain system, which includes both a traditional internal combustion engine and an electric motor. This setup allows the car to utilize both gasoline and electricity for propulsion, depending on driving conditions and power demands.
2. Regenerative Braking:
One of the key features of hybrid cars is regenerative braking. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy from the moving vehicle into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the car's battery pack for later use, rather than being wasted as heat as in traditional braking systems.
3. Seamless Transition:
Hybrid cars are designed to seamlessly transition between the gasoline engine and the electric motor, depending on driving conditions. At low speeds or during idling, the electric motor may take over propulsion duties, drawing power from the battery pack. As the vehicle's speed increases or when additional power is needed (such as during acceleration or climbing hills), the gasoline engine kicks in to provide additional power, either supplementing or replacing the electric motor's output.
4. Types of Hybrid Systems:
There are several types of hybrid systems used in hybrid cars, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits:
Series Hybrid: The gasoline engine acts solely as a generator, charging the battery pack and providing electricity to power the electric motor. The wheels are driven exclusively by the electric motor.
Parallel Hybrid: Both the gasoline engine and the electric motor are connected directly to the transmission, allowing them to work together to drive the wheels. This configuration offers greater flexibility and efficiency.
Plug-in Hybrid: Equipped with larger battery packs that can be charged from an external power source, plug-in hybrids can travel longer distances on electric power alone.
5. Environmental Benefits:
Hybrid cars offer numerous environmental benefits compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. By reducing fuel consumption and emissions, hybrid cars help mitigate air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and dependence on fossil fuels. Additionally, advances in hybrid technology have led to the development of plug-in hybrids and fully electric vehicles, further reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
In summary, hybrid cars work by combining the power of a gasoline engine and an electric motor to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and provide better overall performance. Through innovative technology and smart engineering, hybrid cars offer a compelling alternative to traditional vehicles, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable future on the road.



Comments
Post a Comment